JSON data type in Teradata with examples
Contents
What is JSON?
Javascript Object Notation (JSON) is a text based data format for representing structured data based on Javascript object syntax. It is often used when data is sent from server to webpage. It may contains text, curly braces, square brackets, colons, commas, double quotes, and maybe a few other characters.
JSON example
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
{ firstName:"Peter", lastName:"Andre", age:31, city:"Los Angeles" }; |
JSON data type in Teradata
Teradata providing the the JSON data type to store JSON data in tables. Teradata Database can store JSON records as a JSON document or store JSON records in relational format.Also it provides methods, functions, and stored procedures that operate on the JSON data type, such as parsing and validation.
JSON data type syntax
We can specify the JSON as a datatype for the columns while creating the table in Teradata. The following syntax will be used to define a table column to be JSON type.
|
1 |
JSON <integer> CHARACTER SET <UNICODE/LATIN> <attributes> |
- integer – It specifies the maximum length in characters of the JSON data type.
If we not specify a maximum length, the default maximum length for the character set is used. - CHARACTER SET – The character set for the JSON type can be UNICODE or LATIN. If we not specify a character set, the default character set for the user is used.
- attributes – The following data type attributes are supported for the JSON type.
- NULL and NOT NULL
- FORMAT
- TITLE
- NAMED
- DEFAULT NULL
- COMPRESS USING and DECOMPRESS USING
JSON data type examples in Teradata
Lets create the Employee table with the two column such as Employee_id and details. Here we are defining the details column as JSON data type as below.
|
1 2 3 |
CREATE TABLE Banking_Db.Employee (Employee_id INTEGER, Details JSON(2500) CHARACTER SET LATIN NOT NULL); |
#1.Insert the JSON value to a table
The JSON value should be covered with single quotes while inserting into the table.Otherwise Teradata will throw the error code 3704 with the message as “It is not a valid Teradata SQL token”.
Example :
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
- Employee details passed in the JSON format INSERT INTO Banking_Db.Employee (1568, '{ "firstName":"Peter", "lastName":"Andre", "age":31, "city":"Los Angeles" }'); INSERT INTO Banking_Db.Employee (1892, { "firstName":"James", "lastName":"Charles", "age":25, "city":"New York" }); |
#2.Select the JSON value in a Table
|
1 |
SELECT * FROM Banking_Db.Employee; |
If we select the table which contains the JSON value, It will show in the form of text document in the Teradata SQL assistant.

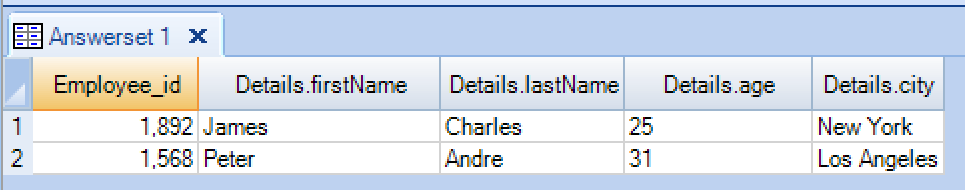
Let’s select the JSON value based on the key column in the JSON text.
Example : Retrieving the JSON value from Teradata
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
SELECT Employee_id, details.firstName, details.lastName, details.age, details.city FROM Banking_Db.Employee; |
Also we can use JSONExtract method to get the Json value based on the key column.But again it will return the results in the form of text document in Teradata SQL assistant.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
SELECT Employee_id, details.JSONExtract('$.firstName') FROM Banking_Db.Employee; -- Use the JSONExtract function in the where condition SELECT Employee_id,details FROM Banking_Db.Employee WHERE details.JSONExtractValue('$.firstName') = 'James' ORDER BY 1; |
#3.Modifying JSON columns in Teradata
The following UPDATE statement sets the details column with the new json value.
Example for UPDATE statement
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
UPDATE Banking_Db.Employee SET details = NEW JSON(' { "firstName":"Justin", "lastName":"Charles", "age":28, "city":"New York" }') WHERE details.JSONExtractValue('$.firstName') = 'James'; |
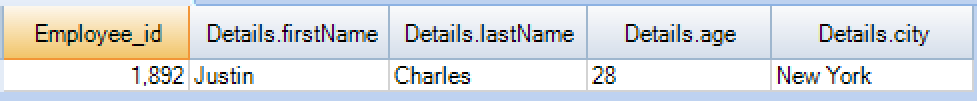
Lets select the Employee table to see the updated JSON value. Previously the employee_id #1892 is assigned to employee which has the first name as James. After the update statement, the new JSON value has updated and employee_id #1892 is assigned to “Justin”.

JSON update statement example in Teradata
#4.Using JSON type in Delete statment
We can specify the JSON value in the delete statement using JSONExtractValue function. We need to cast the JSON value to predefined type that can have relational comparisons performed on it,
The following DELETE statement deletes the record which has age as 31 in the Json value.
Example :
|
1 2 3 |
DELETE Banking_Db.Employee WHERE CAST (details.JSONExtractValue('$.age') AS INTEGER) = 31; |
Lets run the select statement to see the remaining records in the employee table.