Pivot function in Teradata with examples
Contents
PIVOT in Teradata
Pivot function is used for transforming rows into columns in Teradata. It allows us to aggregate and rotate data to create easy-to-read tables that is used for reporting purposes.
To create the pivot table, we need to specify the PIVOT operator in the FROM clause of SELECT statement. Along with PIVOT operator, we can specify other clauses as well with the SELECT query.
Syntax for PIVOT function
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
SELECT * FROM <table_name> PIVOT ( aggr_fn(column_name) AS pvt_aggr_alias FOR column_name IN (expr1 AS expr1_alias_name, expr2 AS expr2_alias_name,...expr_n) ) AS <derived_table_name> |
Syntax Elements
- aggr_fn – An aggregate function that supports a single argument. Example, SUM,COUNT,AVG ..etc
- pvt_aggr_alias – An alias name specified for the aggregate function.
- expr – An expression or column value.
- expr_alias_name – An alias name specified for the values/expressions specified in the IN list.
- derived_table_name – The table name specified for the resultant pivoted table.
PIVOT example in Teradata
Lets create the Quartely_Results table and use the Pivot function to transpose the rows to columns in Teradata.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
CREATE TABLE Finance_DB.Quarterly_Results( Company VARCHAR(20),Product VARCHAR(10), Yr INTEGER,Qtr VARCHAR(3),Sales INTEGER,Cogs INTEGER); SELECT * from Finance_DB.Quarterly_Results; |
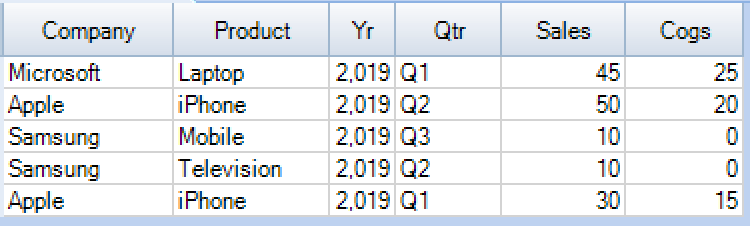
In this table, we can calculate the Sum of Sales and Cogs (Cost of Good Sold) per Quarter using Pivot function as below. The IN list contains the alias name such as Quarter1,Quarter2 & Quarter3. Those alias names are concatenated with the alias name(ss1 &qtr) specified by the aggregate functions to build the column names of the output pivoted table.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
SELECT * FROM Finance_DB.Quarterly_Results PIVOT ( SUM(Sales) as ss1, SUM(Cogs) as sc FOR qtr IN ('Q1' AS Quarter1, 'Q2' AS Quarter2, 'Q3' AS Quarter3) )Tmp; |
Output of Pivoted table
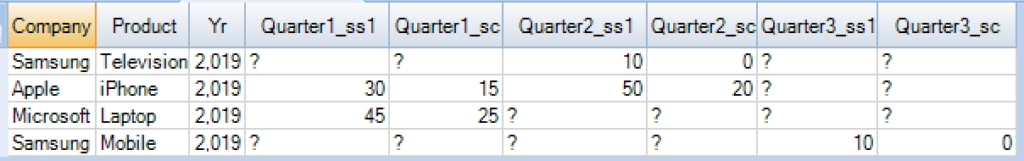
Without using PIVOT function, We can fetch the same results using the SELECT and CASE statements as below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
SELECT * FROM (SELECT Company ,Product ,Yr , SUM(CASE WHEN Qtr = 'Q1' THEN Sales ELSE NULL END )AS Quarter1_ss1, SUM(CASE WHEN Qtr = 'Q1' THEN (Cogs) ELSE NULL END )AS Quarter1_sc, SUM(CASE WHEN Qtr = 'Q2' THEN (Sales) ELSE NULL END)AS Quarter2_ss1, SUM(CASE WHEN Qtr = 'Q2' THEN (Cogs) ELSE NULL END)AS Quarter2_sc, SUM(CASE WHEN Qtr = 'Q3' THEN (Sales) ELSE NULL END)AS Quarter3_ss1, SUM(CASE WHEN Qtr = 'Q3' THEN (Cogs) ELSE NULL END)AS Quarter3_sc FROM Finance_DB.Quarterly_Results GROUP BY Company ,Product ,Yr ) Tmp ; |
Example : Naming columns with the <column_value_list> Values
If we did not specify the column names for pivot table explicitly, the names of the columns are built internally by adding the aggregated column name to the values as below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
SELECT * FROM Finance_DB.Quarterly_Results PIVOT ( SUM(Sales) AS ss1, SUM(Cogs) AS sc FOR (Yr, Qtr) IN ( (2019, 'Q1'), (2019, 'Q2'), (2019, 'Q3') ) )Tmp; |
This is re-written as an the equivalent SELECT query with CASE statement
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
SELECT * FROM (SELECT Company ,Product , SUM(CASE WHEN Yr = 2019 AND Qtr = 'Q1' THEN Sales ELSE NULL END) AS "2019_'Q1'_ss1" , SUM(CASE WHEN Yr = 2019 AND Qtr = 'Q1' THEN Cogs ELSE NULL END) AS "2019_'Q1'_sc", SUM(CASE WHEN Yr = 2019 AND Qtr = 'Q2' THEN Sales ELSE NULL END) AS "2019_'Q2'_ss1" , SUM(CASE WHEN Yr = 2019 AND Qtr = 'Q2' THEN Cogs ELSE NULL END) AS "2019_'Q2'_sc", SUM(CASE WHEN Yr = 2019 AND Qtr = 'Q3' THEN Sales ELSE NULL END) AS "2019_'Q3'_ss1", SUM(CASE WHEN Yr = 2019 AND Qtr = 'Q3' THEN Cogs ELSE NULL END) AS "2019_'Q3'_sc" FROM Finance_DB.Quarterly_Results GROUP BY Company ,Product ) Tmp ; |
Output of Pivoted table with internally build column names
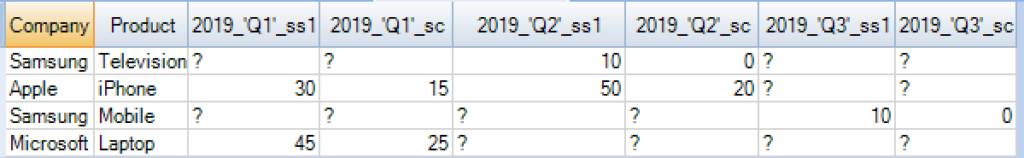
Usage Notes for Pivot function
- Specify one Aggregate function with the PIVOT operator.
- Columns with CLOB, BLOB, UDT, XML, or JSON data types are not allowed with the PIVOT operator.
- If the IN-list contains case-specific values such as ‘abc’ & ‘ABC’, the values are treated the same and an error occurs.
Recommended Articles
- How to use Qualify row number in Teradata?
- How to write a Nested Case statement in Teradata?
- REGEXP_SUBSTR function in Teradata with examples
- REGEXP_REPLACE function in Teradata with examples
